Paytm was the first company to introduce digital payment services in India. It experienced a major boost when the Indian government announced demonetization as a step to fight corruption. During that period, Paytm significantly increased its market share, as people were encouraged to use digital payments more frequently. This situation proved highly beneficial for Paytm business model and established it as a major player in the market.
“The company was founded by Vijay Shekhar Sharma around 2010. It initially started as a mobile recharge service and gradually expanded into various business segments. Around 2014, the company launched digital payment services through the Paytm Wallet. Following that, it ventured into Paytm Payment Services, Financial Services, and Marketing Services.”
How does Paytm make money
Paytm has a strong presence in the digital payments space. With years of experience in this segment, it holds a competitive edge. A significant portion of its revenue comes from its core payment services. In addition to this, Paytm also generates income from its financial services and marketing services. Collectively, these three segments form the foundation of Paytm’s revenue model.”
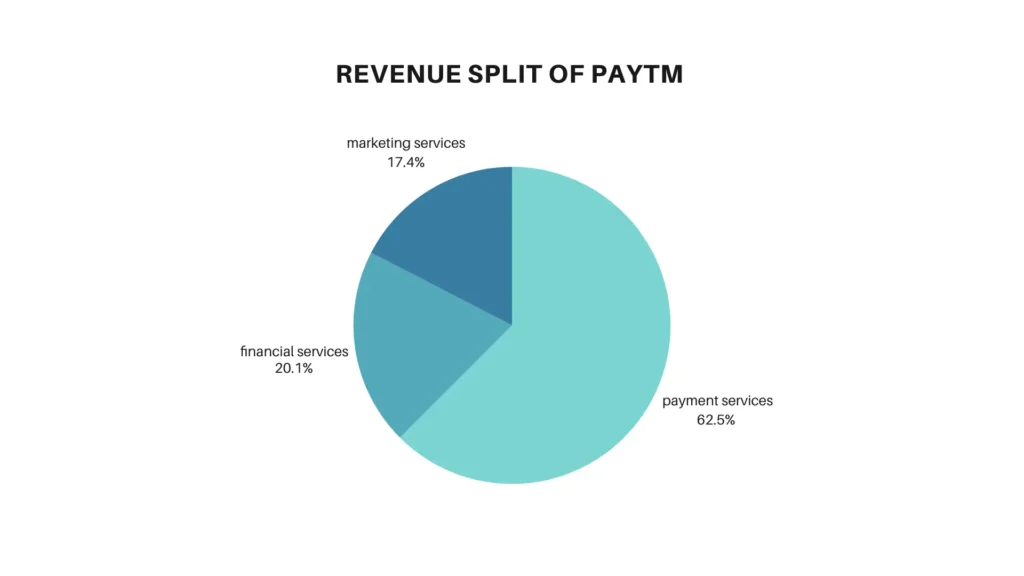
Payment services
Payment services form the core of Paytm’s business, contributing around 62% of the company’s total revenue. Paytm generates income from various aspects of this segment. As the government promotes UPI payments, it also offers incentives to companies like Paytm, which adds to their earnings. Additionally, Paytm earns from the MDR (Merchant Discount Rate) on payments made through Rupay credit cards on UPI.
Another key revenue stream comes from subscription services related to soundboxes and EDC machines. When a customer makes a payment at a shop, these devices provide instant audio confirmation of the transaction. For this service, Paytm charges a subscription fee from merchants. With approximately 1.07 million active soundboxes and EDC devices, this has become a major driver of Paytm’s payment services revenue.”
Financial services
Paytm also has a strong presence in financial services and is continuously exploring new ways to expand this segment. Many shop owners using Paytm soundboxes, as well as individual users, have accounts with Paytm Payments Bank. Through these relationships, the company offers a variety of financial products such as loans, credit cards, and other financial services, generating additional revenue. In 2024, Paytm earned nearly ₹2,000 crore from its financial services segment, contributing around 20% to the company’s total revenue. This segment is expected to grow further, as it offers high margins and promising business potential for the company.”
Marketing services
Paytm is also expanding its marketing services by exploring new business avenues. As most of Paytm’s operations are digital and it has a large user base, the company is leveraging this to generate revenue through advertisements, travel bookings, entertainment services, and deals.
It charges fees for these services, which contributes significantly to its overall revenue. In 2024, marketing services brought in approximately ₹1,738 crore, accounting for around 18% of Paytm’s total revenue.”
Also read; HDFC bank business model
Expenses of Paytm business model
Paytm currently operates at a net loss, as its expenses exceed its revenue. This naturally raises investor curiosity about the company’s revenue sources and expenditure structure. A significant portion of Paytm’s expenses—approximately ₹4,590 crore—goes toward employee costs, accounting for nearly 46% of total expenses.
The company also incurs manufacturing costs, which make up about 41% of expenses. it comes from around ₹3,200 crore on processing charges and software, cloud, and data services, totalling approximately ₹6,43 crore—making it the second-largest contributor to overall costs.
Other notable expenses include ₹735 crore in depreciation, ₹24 crore in finance costs, and about ₹920 crore in marketing and promotional activities all these accounts for the remaining cost of Paytm.
Future Perspective of the Paytm Business
One of the key aspects of Paytm’s business is that it operates entirely in the digital space, which gives it access to significant data and a large base of active users. Since 2020, the company has maintained an average of 400 million monthly transaction users, and in the financial year 2024, it reached approximately 9.6 crore active users—a notable milestone.
With this user base, the company aims to generate revenue through multiple channels. Paytm’s business model is primarily built on three segments: payment services, financial services, and marketing services. While payment services continue to perform as expected, the company is also focusing on increasing user engagement in its financial and marketing service segments to drive further growth.
The company has access to valuable data on how individual users make transactions. Using this data, Paytm offers various types of loans and financial products. Through Paytm Payments Bank, which has a strong base of account holders, the company is able to provide a range of financial services.
This user transaction data is a significant asset, as it enables the company to assess creditworthiness and offer tailored services like credit cards and loans. This approach not only enhances revenue opportunities but also improves targeting and efficiency.
Additionally, Paytm is expanding its marketing services to generate revenue through avenues like entertainment, travel bookings, and more. The company also forms partnerships with other businesses to offer a wider range of products through its platform, including e-commerce offerings. These initiatives contribute to Paytm’s broader growth strategy and support its ambition for long-term, scalable expansion.”
Threat to the Company’s Business Model
Paytm was the first company to introduce digital payments in India and initially emerged as a market leader. However, with the entry of strong competitors like Phone Pe and Google Pay, Paytm has lost a significant portion of its market share in the digital payments space. This decline in market dominance is a key concern and represents a major threat to the company’s business model.”
Additionally, the RBI has imposed restrictions on Paytm’s financial services business due to non-compliance with regulatory guidelines. As a result, the RBI has recently barred Paytm Payments Bank from onboarding new customers or opening new KYC accounts. This has been a major setback for Paytm’s business model, especially in terms of growth in the financial services segment.
Currently, the company is left with only two active revenue streams—payment services and marketing services—to drive business. However, if Paytm successfully addresses all compliance issues and the RBI lifts the restrictions, it could significantly benefit the company and restore growth opportunities in its financial services business.”

2 thoughts on “Paytm business model; How Paytm make money, expenses, Core business , future perspective”