HDFC Bank is regarded as India’s largest private bank, with one of the highest profits in the entire Indian banking industry. It holds a strong domestic market share and has a significant presence in various financial sectors.
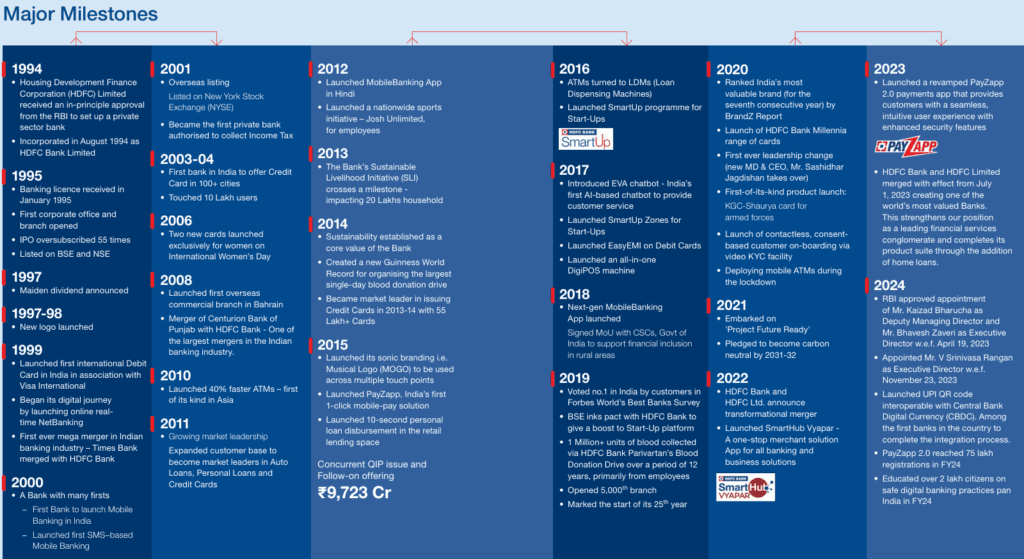
HDFC Limited has an interesting story behind the establishment of HDFC Bank. Initially engaged in the housing finance business, HDFC Limited received approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1994 to set up a private bank after India’s economic liberalization. When HDFC Bank was launched, it provided a steady and robust revenue stream, making it HDFC bank business model one of the strongest entities in the financial sector a
Since HDFC Limited was already a leading financial entity in India, it established various subsidiary companies to drive further growth and revenue. Some of these include:
HDFC Financial Services, HDFC Life Insurance, HDFC ERGO General Insurance, HDFC Asset Management Company, HDFC Securities
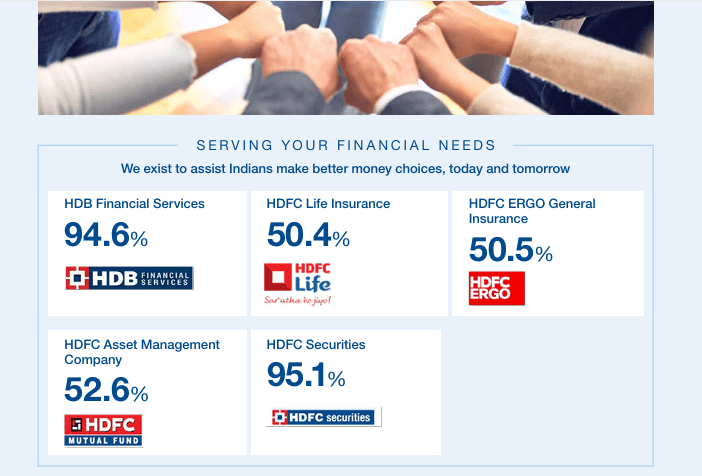
These subsidiaries significantly contribute to HDFC Bank’s overall revenue, strengthening its position in the financial sector and ensuring long-term growth.
The 2022 Merger: A Game Changer
In 2022, HDFC Bank decided to merge HDFC Limited into itself, making HDFC Bank the parent company. This merger was a game changer because the management expected that revenue from HDFC Limited’s strong urban presence would enhance cost-effectiveness and profitability for the bank.
How HDFC Bank Generates Revenue
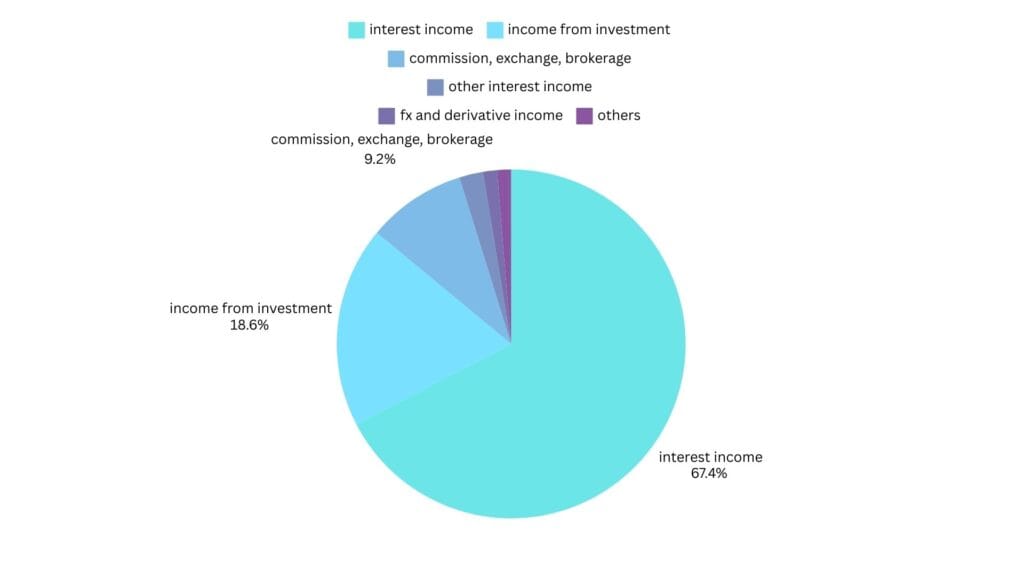
HDFC Bank generates revenue through several streams. However, three major sources contribute nearly 90% of its total earnings: Interest from Advances, Income from Investments, Fees from – Commissions, Exchange, and Brokerage
Let’s explore each in detail:
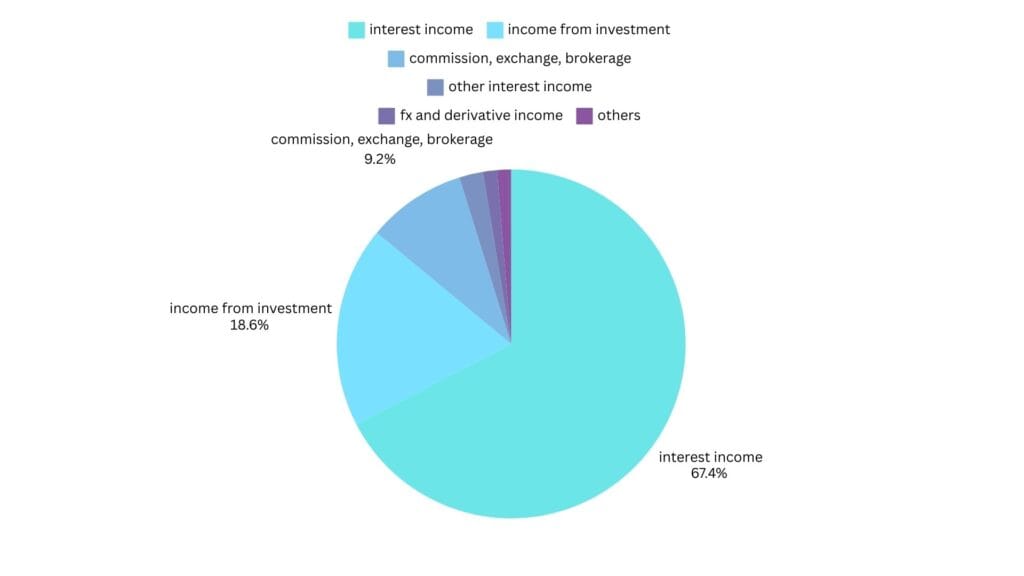
1. Interest from Advances (68%)
A significant portion of HDFC Bank’s revenue comes from interest earned on loans and advances. When customers deposit money in savings accounts or fixed deposits (FDs), the bank utilizes these funds to provide loans such as home loans, personal loans, and mortgages. The interest charged on these loans forms the core of the bank’s revenue, contributing nearly 68% of its earnings.
2. Income from Investments (18.3%)
All banks must comply with RBI regulations by maintaining a portion of their deposits as reserves. These include:
CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio – 4.5%): A portion of deposits that banks must keep in liquid form with the RBI. This amount cannot be invested.
SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio – 18%): A portion of deposits that must be invested in government-approved securities.
For example, if HDFC Bank receives ₹100 in deposits, approximately ₹22-23 must be set aside for compliance. While CRR funds remain with the RBI, SLR funds are invested in secure bonds such as government securities or US-backed bonds. This generates revenue and contributes around 18.3% to the bank’s total earnings.
3. Fees from Commissions, Exchange, and Brokerage (9.2%)
HDFC Bank earns a considerable portion of its revenue from commissions and brokerage fees through its subsidiary businesses, such as insurance and asset management. These financial services contribute approximately 9.2% of the bank’s revenue, making it a vital income stream.
Major Expenses of HDFC Bank
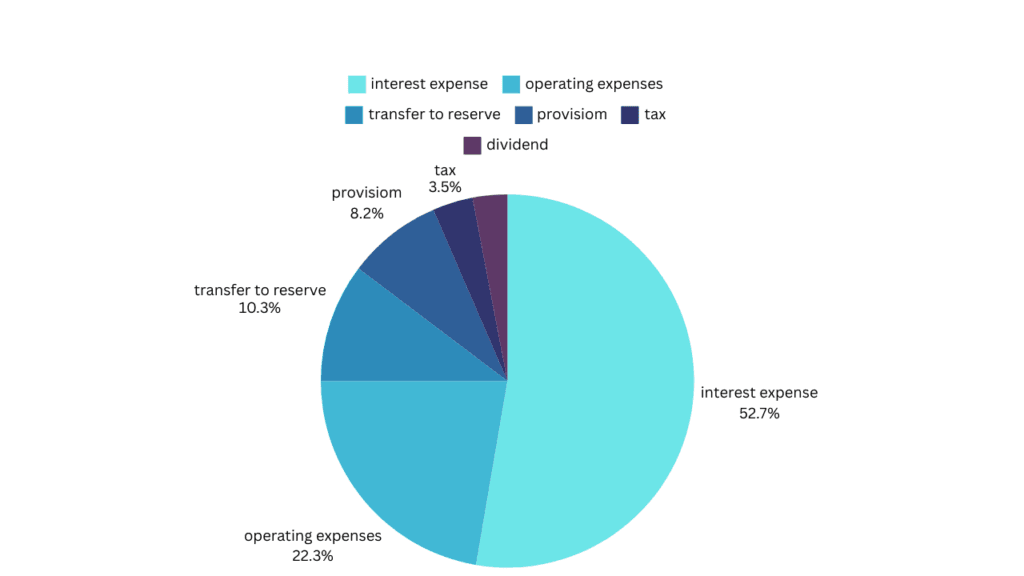
1. Interest Expenses (54%)
A major expense for HDFC Bank is the interest it pays on customer deposits. While the bank earns interest from loans, it must also pay interest to depositors. This is the largest cost component, accounting for nearly 54% of total expenses.
2. Operating Expenses (22.3%)
Operational costs include salaries for employees, infrastructure maintenance, and other administrative expenses necessary to keep banking operations smooth. These expenses make up about 22.3% of the bank’s total costs.
3. Reserves and Provisions
Although not a direct expense, banks set aside a portion of their profits as reserves to ensure financial stability. Maintaining adequate reserves is crucial for long-term business continuity and risk management.
4. Dividend Payments and Taxes
Dividends are distributed to shareholders as returns on their investment, while taxes are paid as part of regulatory compliance. These provisions help in the financial planning of the bank.
Overall, the biggest expenditures for HDFC Bank are interest expenses and operating costs.
Positive Factors of HDFC bank business model
One of HDFC Bank’s biggest strengths is its diversified business model. It operates in multiple financial sectors, including: Asset Management, Insurance, Brokerage
Since these sectors have high future growth potential, HDFC Bank benefits from synergies between its banking services and financial subsidiaries. The bank can cross-sell products to its existing customers, making operations more cost-efficient and profitable.
Additionally, the banking sector is highly competitive, but HDFC Bank holds a strong position due to its ability to bundle services like insurance and asset management with traditional banking products. This gives it a competitive edge over standalone financial institutions.
also read; Foreign Investment; importance, types and Negative impact of foreign investment
Challenges and Negative Factors in HDFC bank business model
1. Slower Growth in Stock Returns
HDFC Bank maintains a steady annual growth rate of 15-20%. However, stock market investors may find the expected 10-12% returns relatively low compared to other high-growth investment opportunities. As a result, some investors may prefer stocks with greater return potential.
2. Changing Investment Preferences
Traditionally, a large part of HDFC Bank’s revenue comes from interest on advances. However, Millennials and Gen Z investors are increasingly shifting towards mutual funds and direct stock investments instead of keeping money in fixed deposits.
This shift could lead to:
Fewer bank deposits, forcing banks to offer higher FD interest rates to attract customers.
Increased interest expenses, as banks would have to pay higher interest on deposits while maintaining competitive lending rates.
These factors could impact HDFC Bank’s profitability in the long run.
Conclusion
HDFC Bank remains a dominant force in the Indian banking sector with a well-diversified business model. Its strong market presence, multiple revenue streams, and strategic mergers ensure stability and growth. However, challenges such as slower stock returns and changing investment patterns could pose long-term risks. Investors should carefully evaluate these factors before considering HDFC Bank as an investment opportunity.


6 thoughts on “HDFC bank business model; Revenue, expense and positive and negative factor of business”