The US inflation data will be released tomorrow on a monthly basis, and it will be closely Nasdaq traders, and Federal Reserve members. They are considering inflation—partly driven by tariffs—as a major factor, which is why there is hesitation in cutting interest rates. This data is extremely important, as it could determine whether measures are taken to lower inflation or if there will be any deviation from the planned interest rate cuts in the USA.
It will have a severe impact on the U.S. economy. If the inflation data comes in very high, it will be extremely negative for economic growth. Rising inflation itself is a serious concern, and to counter it, the Federal Reserve may decide not to implement any interest rate cuts in the future. Such a decision is considered highly significant by most economists in the United States.
Following this trend, the Nasdaq has been hitting new highs every day, as most traders expect that the impact of the tariff war could be highly beneficial for the U.S. economy. This optimism is driving the Nasdaq to higher levels daily. As of today, it has reached around 23,650, marking an all-time high within just two days of trading. Such developments are further boosting investor expectations to even higher levels.
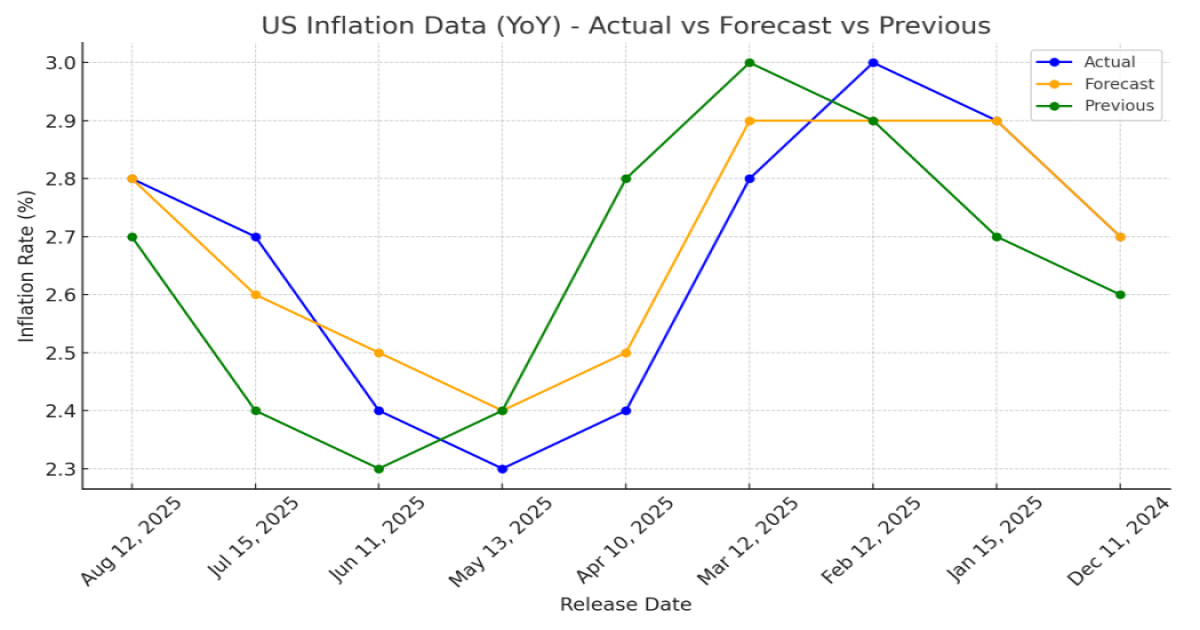
The CPI data for June did not meet expectations, as inflation rose slightly. It was anticipated that June inflation would be around 2.6%, but it came in at 2.7%. After the reciprocal tariff of nearly 10% on global imports in April, inflation stood at 2.3%, then increased to 2.4% in May, and now to 2.7% in June. This trend indicates that the impact of tariffs on inflation is being felt in the U.S. economy.
If inflation continues to rise as expected—currently projected at 2.8% for July—and the data comes in at or above 3%, it will be very difficult for Federal Reserve members to cut interest rates. This is a key factor for the U.S. economy, as such a scenario could lead to higher borrowing costs, potentially disrupting growth and creating uncertainty about the economy’s future due to the impact of elevated Federal Reserve rates.
Citing the need to keep inflation under control, the U.S. administration is repeatedly pressuring the Federal Reserve to lower borrowing costs. They argue that a rate cut would make it easier for businesses to secure loans, boost manufacturing, and support economic growth. With tariffs in place on imports from across the globe, businesses require substantial funding to operate effectively. However, high interest rates are making it difficult for U.S. borrowers to obtain loans from banks, raising borrowing costs for companies looking to expand or hire, which in turn is putting pressure on business activity.
This is why the Trump administration continues to push the Fed to lower interest rates. However, inflation data remains above 2%—the Fed’s target level—prompting caution among Federal Reserve members. Cutting rates in such a scenario is seen as potentially harmful to the economy. As a result, a standoff has emerged between the Fed, led by Jerome Powell, and the Trump administration over the direction of interest rate policy.
Currently, the U.S. interest rate stands at 4.5%, which is considered high for a developed economy like the United States. There has been no rate cut throughout 2025, and this is why the U.S. administration’s first reaction is directed at the Federal Reserve. Another important factor is that negotiations between countries are ongoing regarding tariffs, which also plays a significant role.
Also read – Inflation Impact; How to measure, steps taken to curb inflation and how it affects stock market
Currently, the U.S. interest rate stands at 4.5%, which is considered high for a developed economy like the United States. There has been no rate cut throughout 2025, and this is why the U.S. administration’s first reaction is directed at the Federal Reserve. Another important factor is that negotiations between countries are ongoing regarding tariffs, which also plays a significant role.
At the moment, U.S. inflation data is crucial, especially since it has been three months of consistent increases, making inflation a key concern. Many goods that could potentially raise U.S. inflation have been exempted from import tariffs in most countries, but other products still remain under tariff restrictions. All these factors are now taking center stage, and how the upcoming inflation data turns out will be very important. It will be closely considered by both U.S. monetary policy makers at the Federal Reserve and economists.
A significant event is also set to take place this week, as U.S. President Donald Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin are scheduled to meet in Alaska to discuss the ongoing trade dispute and the Russia–Ukraine ceasefire. This meeting will be closely monitored, as any failure to meet Trump’s expectations could have consequences. If an agreement on a ceasefire is reached, it would be positive for both the U.S. economy and global growth.
The U.S. has already imposed an additional 25% tariff, citing the purchase of Russian crude oil, and has also warned countries buying Russian crude that they could face further tariffs. These measures are affecting U.S. imports and are closely linked to the nation’s inflation trends, which ultimately influence Federal Reserve monetary policy. All these factors are interconnected, making the outcome of the U.S.–Russia meeting critical—not only regarding the ceasefire but also in terms of U.S. policy toward China, which continues to purchase Russian crude oil.
1 thought on “US Inflation Data Ahead – Key Focus for Markets and Policymakers”